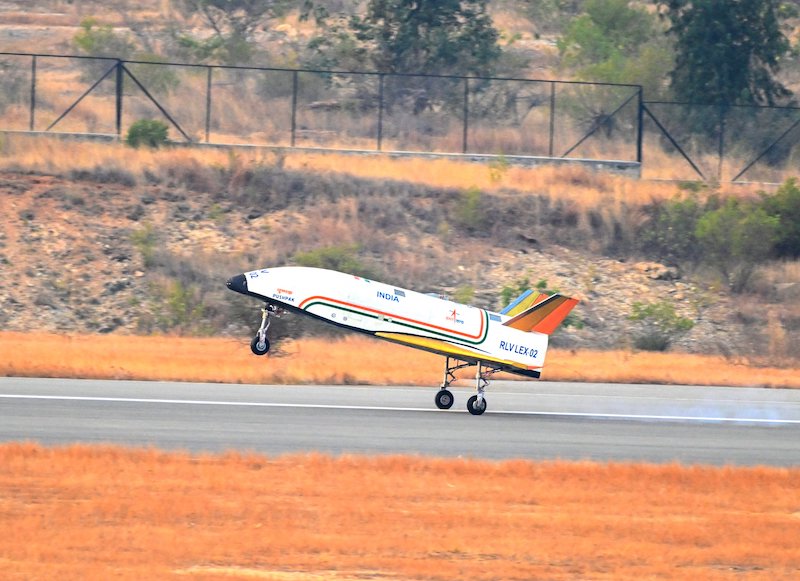
RLV LEX-02 vehicle during landing. (Photo: Isro)
RLV LEX-02 vehicle during landing. (Photo: Isro)
New Delhi: The Indian Space Research Organization has achieved another breakthrough in its efforts to develop a reusable launch vehicle (RLV) with the successful completion of the RLV-LEX-02 experiment. This mission, conducted on Friday, at the Aeronautical Test Range in Chitradurga, Karnataka, builds upon the success of the RLV-LEX-01 mission last year.
Nicknamed “Pushpak” after the mythical flying chariot, the RLV-LEX-02 experiment focused on demonstrating the vehicle’s autonomous landing capabilities under challenging conditions. Unlike its predecessor, which was released at a predetermined altitude and trajectory, the LEX-02 was released from a helicopter, introducing deliberate deviations in its initial position and speed.
This simulated the high-stress scenario of a reusable launch vehicle returning from space and needing to autonomously adjust its course for a safe landing.
RLV-LEX-02:
— ISRO (@isro) March 22, 2024
The approach and the landing. pic.twitter.com/hI9k86KiBv
The mission successfully simulated the approach and high-speed landing conditions of an RLV returning from space1. Isro stated that the mission revalidated the indigenously developed technologies in the areas of navigation, control systems, landing gear, and deceleration systems essential for performing high-speed autonomous landing of a space-returning vehicle.
The winged body and all flight systems used in the previous RLV-LEX-01 mission were reused in the RLV-LEX-02 mission after due certification and clearances. This demonstrates the reuse capability of flight hardware and flight systems.
The director of Isro’s Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, Dr S Unnikrishnan Nair, said through this repeated success, Isro could master the terminal-phase manoeuvring, landing, and energy management in a fully autonomous mode, which is a critical step towards future orbital reentry missions
RLV-LEX-02: A video collage.
— ISRO (@isro) March 22, 2024
Details:https://t.co/XftP6gaM36
Mighty @IAF_MCC and various ISRO Centres/Units like LPSC, IISU, SAC, SDSC-SHAR, ISTRAC, URSC, etc. fueled the success. pic.twitter.com/IUanvewcaw
The successful landing of the LEX-02 signifies a significant milestone for Isro. It validates the robustness of the vehicle’s navigation, control systems, and landing gear, all of which are crucial for a safe and controlled return from space. Notably, the mission also emphasizes the reusability aspect. The winged body and flight systems used in the LEX-01 were refurbished and employed again in the LEX-02, demonstrating the cost-effectiveness of this technology.
This achievement marks a significant step forward for Isro’s ambitions in space exploration. Reusable launch vehicles have the potential to revolutionize space travel by drastically reducing launch costs, as Elon Musk’s SpaceX is doing. Currently, expendable rockets are used for most space missions, leading to a significant loss of hardware after each launch.
With reusable vehicles, the launch cost can be brought down considerably, paving the way for more frequent and cost-effective space missions.
Isro is already known for its cost-effective space launches. It has been successful in bagging several international space-launch contracts in the past due to its highly competitive pricing and excellent track record of success.
India’s scientific community has lauded Isro’s latest success with the RLV programme. Experts believe this technology holds immense potential for the future of Indian space exploration, enabling more ambitious and cost-effective missions in the years to come.